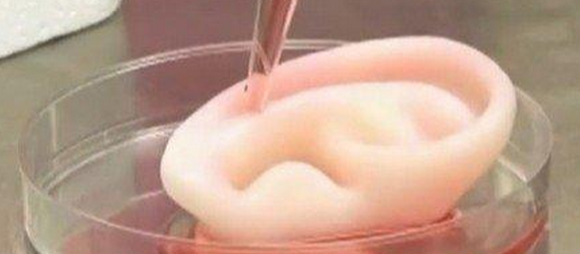
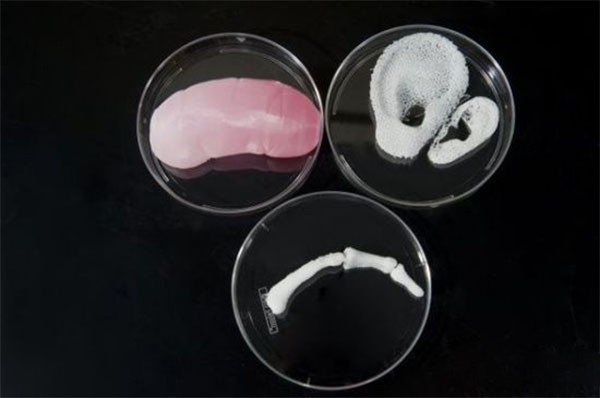
From November 2016 to the present, the news of Blu-ray Inno has been constantly leaked in the 3D printing circle. In early December 2016, after the Antarctic Bear revealed that Blu-ray Inno will conduct a blood vessel 3D printing results conference, Blu-ray development stocks were suspended. In the 2017 New Year's Eve, we will strive to launch clinical implantation in the human body in 2017. 3D printing originated in the 1980s and has developed rapidly in recent years. It is known as "one of the important symbols of the third industrial revolution." Bio 3D printing is a branch of 3D printing and is currently embarking on a new round of research at home and abroad. Below we give a brief introduction to biological 3D printing. First, what is biological 3D printing Bio-3D printing is based on the principle of “additive manufacturingâ€, with the special biological “printer†as the means, processing active materials including cells, growth factors, biological materials, etc. as the main content, interdisciplinary aiming to reconstruct human tissues and organs. A new type of regenerative medicine engineering technology across the field. It represents one of the highest levels of current 3D printing technology. Second, the development of biological 3D printing technology Since its inception in 1995, the development of bio 3D printing technology has gone through four levels. The first level: the printed products do not enter the human body, mainly including some medical models and medical devices used in vitro, and have no biocompatibility requirements for the materials used ; the second level: the materials used have good biocompatibility. However, it cannot be degraded, and the product becomes a permanent implant after being implanted into the human body; the third level: the material used has good biocompatibility and can be degraded. After the product is implanted into the human body, it can interact with human tissues to promote tissue regeneration. The fourth level: using living cells, proteins and other extracellular matrices as materials to print bioactive products, the ultimate goal is to create tissue. ,organ. This is the highest level of bio 3D printing. At this stage, the first to third levels of technology development has been relatively mature, and has entered the practical application level. The first level of application includes personalized surgical models of neurosurgery and spinal surgery, prostheses, and the like. The second level of application includes individualized permanent implants such as artificial ear implants, mandibular grafts, and the like. The vertebral body grafts printed by 3D technology in the Third Hospital of Beijing Medical University in 2014 also belong to this category. The third level uses biodegradable biocompatible materials to create bionic tissue engineering scaffolds. Tsinghua University team uses low-temperature deposition forming technology to produce bone scaffolds with graded pore structure, which can achieve up to 4 levels of pores, which is beneficial to the growth of various cells and is at the world's leading level. The fourth level, also known as "cell printing" or "organ printing," is a modern biological 3D printing. In comparison, the first three levels can be referred to as "rapid prototyping." The concept of cell printing was first proposed by Professor Thomas Boland of Clemson University in the United States in 2000 and was successfully implemented for the first time in 2003. In 2004, the team obtained a patent for cell printing and licensed it to Organovo, which is listed on the NASDAQ, which is currently the world leader in bio 3D printing. Since the author's doctoral tutor is Professor Boland, the author participated in the work, and the published papers received wide attention. Third, the clinical needs and scientific significance of biological 3D printing In the United States, one patient died every 1.5 hours because he could not wait for a proper organ transplant, and there are more than 8 million tissue repair-related surgeries every year. The goal of bio 3D printing technology is to solve the problem of tissue and organ shortage. The human body is a combination of a variety of cells and matrix materials in a specific way, with a high degree of complexity. There are more than 250 kinds of cells that make up the human body, and only one kidney contains more than 20 kinds of cells. Cartilage tissue is a relatively simple tissue with few cell types and no blood vessels and innervation. In 1994, scientists believed that tissue engineering technology could solve the technique of organ reconstruction. At that time, the preferred target was to make skin or cartilage tissue, but there has been no real success so far. Bio 3D printing technology may be one of the solutions.
95.0% OPC Grape seed extract is one kind of Grape Seed Extract which is our Key product. It is a purple powder and was producted by extracting,concentrating and drying;from the seeds of Grape. Grape Seed Extract,Grape Seed Extract Powder,Nature Grape Seed Extract,95% Grape Seed Extract Shaanxi Kepler Biotech Co.,Ltd , https://www.keplerherb.com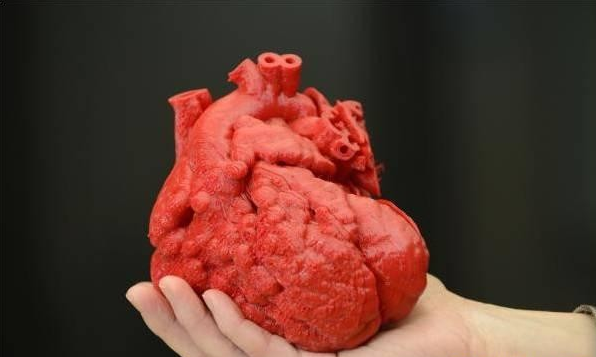
The omponents are mainly phenolic acid such as procyanidins,catechin,epicatechin,gallic acid, epigallocatechin gallate and so on.
Grape seed is the seed of grape, after the separation of grape skin, grape stalk product. Grape seed contains amino acid, vitamin and mineral to wait.
Grape seeds contain polyphenols (GPS), mainly catechins and proanthocyanidins.Catechin compounds, including catechin, epicatechin and their gallate esters, are the main monomers of grape seeds and the constituent units of proanthocyanidin oligomers and polymers.
Grape seeds are rich in oil, accounting for about 12% ~ 15% of its weight. Oil contains a lot of unsaturated fatty acids, among which the content of linoleic acid is between 58% ~ 78%.Grape seeds also contain a small amount of volatile components, most of which are alcohols, phenols and terpenoids, all of which have high biological activity.In addition to the above mentioned substances, grape seeds also contain crude protein, amino acids and vitamins A, E, D, K, P and A variety of trace elements, such as calcium, zinc, iron, magnesium, copper, potassium, sodium, manganese, cobalt and so on.