High-throughput, low-cost SNP, mutation or methylation detection methods - HRM technology applications HRM introduction HRM technology is a high-resolution melting analysis technique, which is a new genetic analysis method for mutation scanning and genotyping. Based on efficient and robust PCR technology, HRM is not limited by mutated base sites and types, and does not require sequence-specific probes. By running high-resolution melting directly after PCR, sample mutations and single nucleotide polymorphisms can be completed. - Analysis of SNP, methylation, HLA matching, and the like. HRM technology has received widespread attention due to its simple and fast operation, low cost of use, and accurate results, enabling true closed-tube operation. HRM principle The main principle of HRM is to analyze the sample according to the length of the DNA sequence, GC content and base complementarity, and use high-resolution melting curve to analyze the sample. The high temperature uniformity and temperature resolution make the resolution accurate to a single base. The distinction between differences. With the advent of high-precision PCR instruments (LightCycler® 480 and Rotor-Gene 6000) and saturated dyes (LC Green, Eva Green, etc.), the popularization of HRM technology has become possible. Screening for ï‚•SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism). ï‚• Gene mutation scans, including deletions, duplications, and point mutations. ç› Screening for new mutations. ç› Screening for methylation. Screening of specific mutations in genetic breeding, discovery of unknown mutations. ï‚• HLA genomic matching, allele frequency analysis, species identification, cultivar identification, methylation research. ï‚• Forensic identification, paternity testing. Studies on the polymorphic loci associated with animal and plant quality. Plant stress resistance, mutation and trait association studies. HRM features ï‚• High throughput: 10-384 samples can be detected simultaneously, suitable for large samples, multiple SNPs, multiple mutation sites and multi-site methylation scans. ï‚• High sensitivity: In the tumor research, the mutation rate of the sample with low mutation rate is detected, and the mutation of 0.1% of the mutant sample is detected at the lowest, that is, one mutant cell of 1000 normal cells is detected, which is suitable for mutation detection in surgery and other trace tissues. The detection sensitivity is much higher than 25% of "PCR+sequencing", that is, at least 25 mutant cells in 100 normal cells, and sequencing is only applicable to surgical tissues. 特异性 Good specificity: PCR products do not require subsequent processing, and the specificity is as high as 100%. Directly unknown heterozygous mutations have an accuracy of 100% and a specificity of 100%. The accuracy of the direct unknown homozygous mutation was 96%, and the accuracy of the unknown unknown homozygote was 100% using the unlabeled probe rapid genotyping method. é‡å¤ Good repeatability: repeatability 100% ï‚• Wide range of use: It is not limited by base sites. In addition to detecting known mutations, unknown mutations can also be detected. é‡å¤ Good repeatability: Sample PCR and HRM analysis are performed directly in the same tube to achieve closed-tube operation to avoid cross-contamination. ï‚• Easy to operate: only need to design specific primers, no sequence-specific probes, no sequencing, and no limitation on the location and type of mutated bases. ï‚• Low cost: Simplify operation time and steps, greatly reduce costs, and the detection cost is much less than sequencing and Taqman probe technology. ï‚• Wide range of specimens: It can be used for fresh or alcohol-fixed, paraffin-embedded surgical specimens. It can also be used for the detection of microscopic puncture or biopsy specimens, blood specimens, stool specimens and other non-surgical specimens. Traditional ï‚“ PCR+ sequencing methods are difficult to detect in most patients who cannot be operated. ï‚• Other: Only detect the change of fluorescence intensity in PCR samples, do not consume any PCR samples, no pollution, PCR products can be analyzed downstream, which is very suitable for pre-synthesis screening such as SNP and methylation before sequencing. HRM application example SNP detection Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) refer to changes in single nucleotide bases, including substitutions, translocations, deletions, and insertions, resulting in polymorphisms in nucleic acid sequences. In the nucleotide sequence of the same chromosome or the same site of different individuals, most of the nucleotide sequences are identical and only one base is different. This is the SNP. SNPs are more abundant in the human genome and occur more frequently, so they are considered to be a new generation of genetic markers following microsatellites. HRM detection SNP technology is based on denaturation of PCR-amplified products over a range of temperatures, during which time the fluorescence signal in the system is detected in real time. The fluorescence value can be plotted as a function of temperature. Each piece of DNA has its own unique sequence, and thus has a unique melting curve shape, like DNA fingerprinting, with high specificity, stability and repeatability. According to the curve, wild type homozygotes, heterozygotes and mutant homozygotes are accurately distinguished (below). There are many ways to detect SNPs. Methods with lower cost and greater throughput are mostly limited to known, specific sites, such as the Taqman probe method. Both the analysis of known sites and the search for unknown sites are generally carried out by PCR+sequencing, which is costly and complicated. HRM technology is a low-cost, high-throughput, fast, and site-independent detection method that is the best choice for SNP screening. Methylation detection DNA methylation is a covalent modification that often occurs on the C pG island of the DNA sequence, which allows gene expression to be inhibited and inherited. In pathological tissues such as tumors, the characteristic methylation status of specific genes can be used as an important marker for early diagnosis. Methylation assays include specific P CR, Northern blotting, microarrays, etc. Sequencing is a standard for sheet metal, but these methods are low throughput, costly, time consuming, and difficult to standardize. HRM detection of methylation has the advantages of high throughput, simple operation, high sensitivity, high reproducibility, low cost, and limited height of detection sites. It will be used in genetics, oncology and other clinical research and clinical applications. Provide even greater help. Mutation screening HRM is characterized by high specificity and high sensitivity, and the detection sensitivity can reach 1%-0.1%. Screening of large numbers of samples and multiple mutation sites is more convenient and cost-effective than traditional heterogeneous methods (such as dHPLC) because the latter needs to transfer amplification products to another instrument for mutation analysis. . HRM screens for unknown mutations on any amplicon without the need to identify primers or probes of different alleles, independent of the location and type of mutated bases, allowing screening and scanning of unknown mutations It is also possible to analyze known mutations. Therefore, compared with the quantitative probe method of mutation analysis and other types of rapid mutation analysis, the application surface has been greatly expanded, and the cost has been greatly reduced. It has become a hotspot of genetics and methodology research and application in foreign countries in recent years. Figure: HRM analysis of a 219 bp human MBL-2 gene fragment (384 samples) showing the four major gene types (blue, red, green, and olive green) and two minority sample genotypes (orange and red) purple). ï¬Other applications Sample processing: ï‚• Tissue specimen: take 50mg of fresh tissue block, one is stored and transported with liquid nitrogen or dry ice, and can be placed in a frozen tube containing RNAlater (provided by our company), stored at 4°C and stored in regular ice pack. 穿刺 Puncture or biopsy specimen: the treatment is the same as above. é…’ç²¾ Alcohol fixed specimens: For those who cannot send fresh specimens, please take the specimens from the operating table and immediately remove the tumor specimens (≥5mm3) and put them in the container (such as plastic bottles with lids). 75% of the ethanol is fixed immediately, ensuring that the volume of the alcohol is about 5 times that of the specimen. ï‚• Paraffin-embedded tissue sections: 10 tissue sections (area >10 mm × 10 mm, thickness 5-10 μm) are required. The slides are stored in a cassette and transported at room temperature. If the organization is too small, please increase the number of samples sent for inspection as appropriate. 血液 Blood sample: Take 5ml anticoagulation, obtain plasma, and transport it in a regular ice pack at 4°C. 胸 Thoracic and ascites: add 1 ml of 75% alcohol after centrifugation of the tumor. 粪 Feces: 10 g of feces were collected and genomic DNA was collected by column centrifugation. references ï‚•ï€ Oliver Geulen, Christian Weilke, Michael Hoffmann. The LightCycler 480 real-time PCR system: a versatile platform for genetic variation research. Nature Methods 5, (29 February 2008) doi:10.1038/nmeth.f.207. Nosiheptide Feed Additives,Nosiheptide Antibiotics,Nosiheptide Growth Prompter,Nosiheptide Poultry Shandong Shengli Bioengineering Co., Ltd , https://www.shenglipharm.com
HRM application 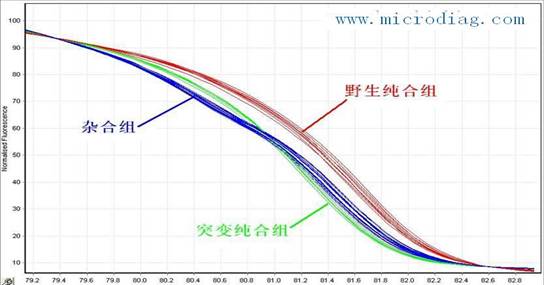

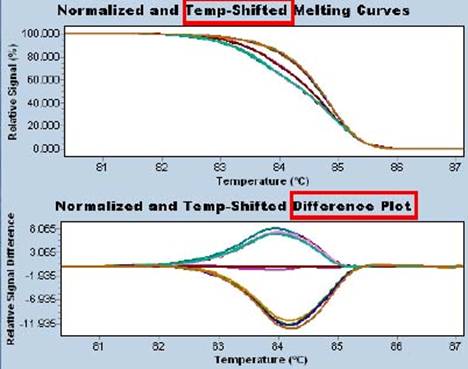
High Resolution Melt (HRM) is a new technology for detecting C pG sites in epigenetics that distinguishes methylation differences in individual bases (below). 
Genotype identification in plant and animal quality and breeding: The HRM method quickly and effectively solves the problem of determining whether the genotype of the parent is the same, whether there is a genetic mutation in the novel trait.
HLA genomic matching: HLA matching of organ transplantation, HLA genotype determination between siblings, application examples: rapid determination of the type of HLA highly polymorphic loci, and HLA before heterologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in non-parental relationships Genotype confirmation.
Allele frequency analysis : SNP frequency analysis, etc.
Species identification, variety identification : rapid identification of microbial varieties and species; identification of animal and plant varieties. Application example: Identification of clinical bacteria. Real-time amplification of 16SrRNA is performed on cultures of clinical bacteria, and HRM analysis is performed. The melting curve pattern of each species is the molecular fingerprint of the species, so that the bacteria can be identified according to the difference of HRM.
Forensic identification, paternity testing : detection of single nucleotide polymorphism SNP identification, insertion/deletion polymorphism DIP identification. Application examples: HRM is used in forensic SNP and DIP identification, assisting crime identification, paternity testing. Compared to traditional identification methods, HRM is a simple, inexpensive, high-throughput method for the identification of biallelic molecular markers.
ï‚•ï€ The LightScanner System: Ultra Fast Mutation Discovery and Gene Scanning Nature Methods Application Notes (2 May 2006) doi:10.1038/an1611.
ï‚•ï€ Erali M, Voelkerding KV, Wittwer CT. 2008. High resolution melting applications for clinical laboratory medicine. Exp Mol Pathol 85:50–58.
ï‚•ï€ Wojdacz TK, Dobrovic A, Hansen LL. Methylation-sensitive high-resolution melting. Nature Protoc. 2008;3(12):1903-8.
ï‚•ï€ Fukui T, Ohe Y, Tsuta K, Furuta K, Sakamoto H, Takano T, Nokihara H, Yamamoto N, Sekine I, Kunitoh H, Asamura H, Tsuchida T, Kaneko M, Kusumoto M, Yamamoto S, Yoshida T, Tamura T. Prospective study of the accuracy of EGFR mutational analysis by high-resolution melting analysis in small samples obtained from patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2008 Aug 1;14(15):4751-7.
ï‚•ï€ Smith GD, Chadwick BE, Willmore-Payne C, Bentz JS. Detection of epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutations in cytology specimens from patients with non-small cell lung cancer utilising high-resolution melting amplicon analysis. J Clin Pathol. 2008 Apr ;61(4):487-93.
ï‚•ï€ Takano T, Ohe Y, Tsuta K, Fukui T, Sakamoto H, Yoshida T, Tateishi U, Nokihara H, Yamamoto N, Sekine I, Kunitoh H, Matsuno Y, Furuta K, Tamura T. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutation detection Using high-resolution melting analysis predicts outcomes in patients with advanced non small cell lung cancer treated with gefitinib. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13(18 Pt 1):5385-90.
ï‚•ï€ Simi L, Pratesi N, Vignoli M, Sestini R, Cianchi F, Valanzano R, Nobili S, Mini E, Pazzagli M, Orlando C. High-resolution melting analysis for rapid detection of KRAS, BRAF, and PIK3CA gene mutations in Colorectal cancer. Am J Clin Pathol. 2008;130(2):247-53.
ï‚•ï€ Chagné D, Gasic K, Crowhurst RN, Han Y, Bassett HC, Bowatte DR, Lawrence TJ, Rikkerink EH, Gardiner SE, Korban SS. Development of a set of SNP markers present in expressed genes of the apple. Genomics. 2008 ;92(5): 353-8.