Theoretically, highly specific, highly sensitive immunoassays can be obtained using well-selected affinity-purified antibodies. However, due to economic reasons or the lack of suitable reagents, many workers use low purity preparations, which typically contain antibodies that cross-react with other components of the assay. It has been found that in the case of antibodies against human IgG antiserum, the antibody contains unwanted antibody cross-reactivity. However, when affinity-purified antiserum was used, the cross-reaction was not significant. To study any ELISA system, in order to control unwanted cross-reactions, it is necessary to use affinity-purifying reagents. The use of anti-IgG serum antibodies as coated antibodies sometimes makes the background very low, but it is 50-100 times less sensitive than using only affinity-purified products. It is important to apply blocking reagents in highly sensitive experiments. The final selection of non-affinity pure anti-IgG serum antibodies is based on the assumption that the coated antibody or the bound human IgG (antigen) cross-reacts with the indicator antibody, and the excess serum of the same animal as the indicator antibody can be blocked. Unwanted binding of the enzyme-labeled antibody. However, small amounts of IgA and IgG in human serum albumin interfere with detection. Human serum albumin is only suitable for the determination of IgE. Similarly, bovine serum albumin cannot be used. Because it contains trace amounts of bovine IgG. The effect of anti-serum antibodies and affinity-pure antibodies on the results of the ELISA sandwich assay can be seen from the experiments below. Experiment a: The coated antibody was a crude sheep anti-human IgG antibody, and the indicator antibody (detection antibody) was a crude goat anti-human IgG antibody. Experiment b: The coated antibody is an affinity pure sheep anti-human IgG antibody, and the indicator antibody (detection antibody) is a crude goat anti-human IgG antibody. Experiment c: The coated antibody is a crude sheep anti-human IgG antibody, and the indicator antibody is an affinity pure goat anti-human IgG antibody. Experiment d: Both the coated antibody and the indicator antibody were affinity-purified rabbit anti-human IgG antibodies. In the experiment, 5% serum (the same species source as the indicator antibody) was used for blocking, and the other sandwich ELISA steps were the same. The results showed that when crude anti-IgG serum antibodies were used at both ends of the sandwich method (such as the experimental a curve), the background was high and the slope of the curve was not significant. Although this type of antibody can be successfully applied, the problem is that one antibody binds to another. It may happen that the goat indicates that the antibody binds to the sheep-coated antibody because the excess of goat serum in the dilution does not reduce the background value. When affinity-purified coated antibodies were applied (as in the experimental b-curve), the background was appropriately reduced and a standard curve was formed. However, most workers believe that the background is still high and the scope of work is limited (2-60 ng/ml). When an affinity-purified indicator antibody is used in combination with a crude coated antibody (such as the experimental c-curve), the background is much lower, but the sensitivity is about 100-200 ng/ml, and the working range is still limited. When the affinity-purified antibody is used completely (such as the experimental d-curve), the background is low, the sensitivity is greatly improved, and the working range is wide (2-500 ng/ml). Recommend more exciting articles: S. aureus CRISPR/Cas9 monoclonal antibody, a variety of experimental applications! Http:// Veterinary drugs: refers to substances (including medicated feed additives) used to prevent, treat, diagnose animal diseases or purposefully regulate animal physiological functions. Veterinary medicine,Niclosamide for Sale,Niclosamide for Humans,Albendazole 400 Mg,Oxfendazole for Dogs Xi'an Henrikang Biotech Co.,Ltd , https://www.xianhenrikangbio.com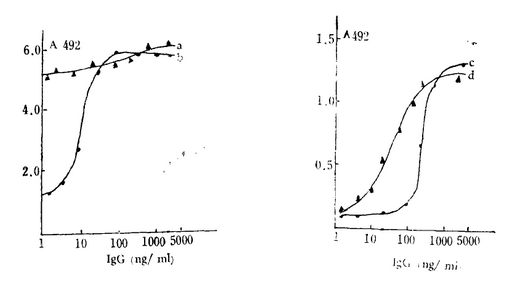
Recommended C-reactive protein (CRP) ELISA kit for high performance for more efficient detection! Http://
The HDAC11 selective inhibitor recognized by Nature, HDAC11 analysis is more effective! http://
Ultra-sensitive StrandBriteTM RNA Quantitation Kit for more accurate RNA! Http://
Veterinary drugs mainly include: serum products, vaccines, diagnostic products, micro-ecological products, Chinese herbal medicines, proprietary Chinese medicines, chemicals, antibiotics, biochemical drugs, radioactive drugs and topical pesticides, disinfectants, etc. veterinary drug
Also known as veterinary drugs or animal drugs, in a narrow sense, it refers to drugs for livestock and poultry, and in a broad sense, it refers to drugs that prevent and treat all animal diseases except humans and promote their growth and reproduction. The research and development of veterinary drugs and human drugs promote each other and develop synchronously.
China's "Handbook of Veterinary Drugs" (1977 edition) contains APIs and a total of 1,300 varieties, the US "Veterinary Drug Index" contains 460 types of veterinary APIs, the "British Veterinary Pharmacopoeia" contains 210 types of APIs, and more than 130 kinds of preparations and 40 kinds of biochemical immune products. In 1979, Japan produced, sold and imported about 1,900 varieties of veterinary drugs.