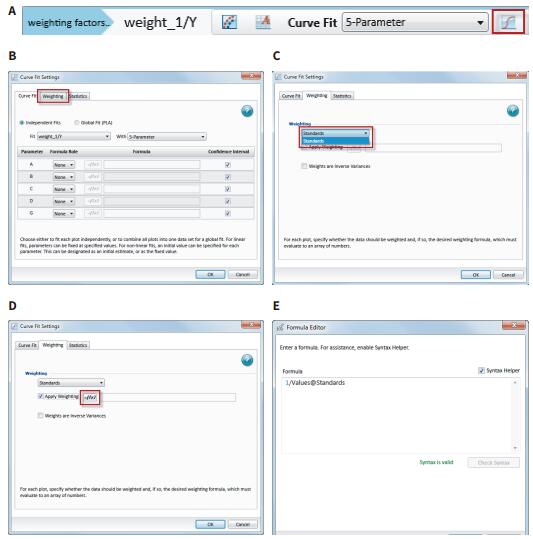
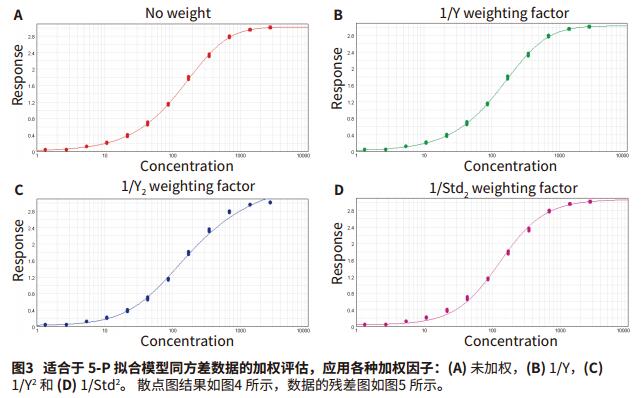
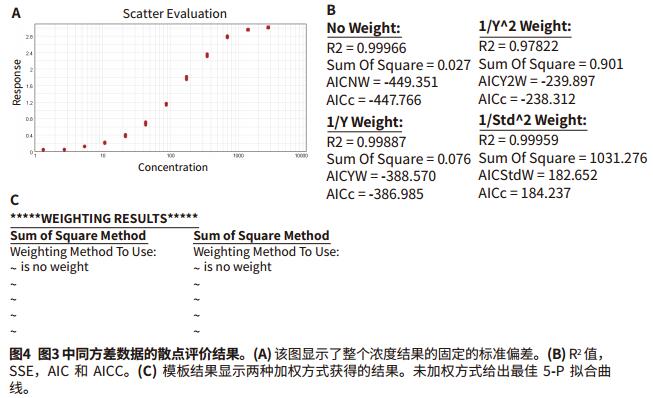
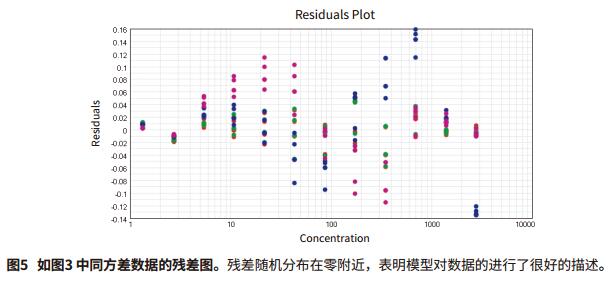
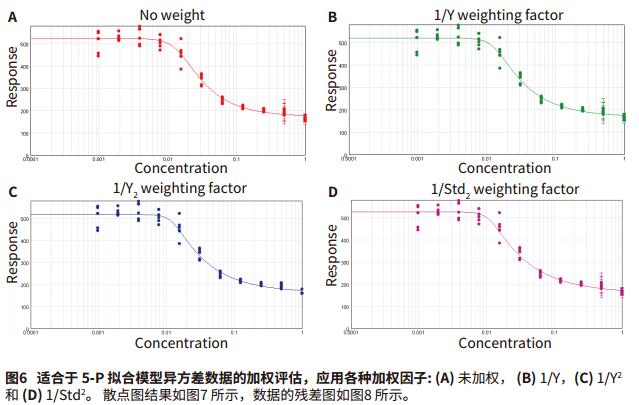
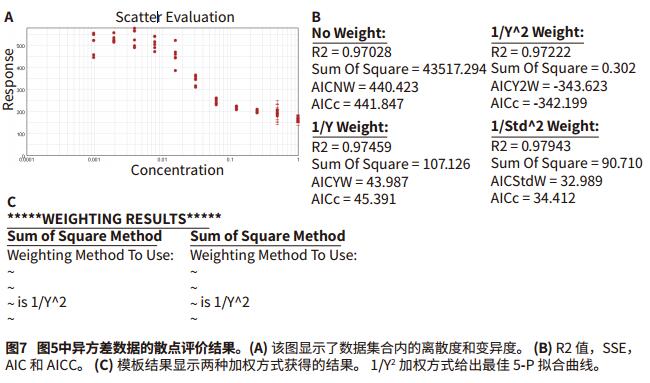
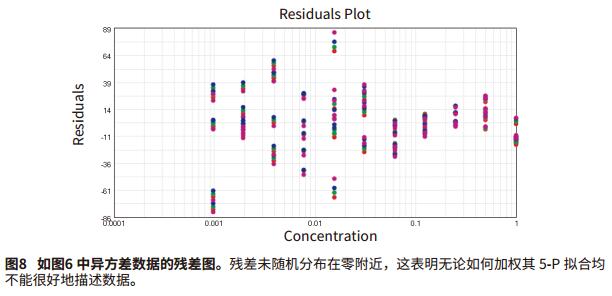
Foreword Choosing the right weighting factor is critical to obtaining the best curve fit, and obtaining curve fitting parameter values ​​makes the curve-fitting model as close as possible to the actual measured data points. Weighting will affect the extent and impact of data points at each concentration, or a particular data point or curve weight is a way to model the error in the data and has been used to process different curves. Differences in absolute errors between different data points, such as four-parameter and five-parameter concentration effect curve fitting. As the concentration increases, the absolute error at the top of the fitted curve is typically greater than the bottom of the curve, increasing the variability of the reaming. A large standard deviation at the top of the fitted curve affects the curve fit and the estimated value of the curve parameters. Choosing the right weighting factor will allow you to better adjust the curve fit so that both the minimum variance and the larger variance can be applied. It is important to understand how to select and apply the correct weighting factors in the distribution data set. If you don't know the weighting of the variation, this application will show you how to use various weighting functions. Advantage - Choose up to 21 curve fits When to use weighting When there is a sufficient amount of data, after obtaining the best curve fitting method based on method development or method verification, the curve is then weighted and the appropriate weighting factor is selected to process the curve. In all curve-fitting models, X (usually concentration) is the independent variable and Y (usually the response value) is the dependent variable. For the same variance data, the standard deviation of all sample concentrations is the same. The best fit is to use a weighting factor for weight fitting. However, the weighting weight becomes very significant for the heteroscedasticity, that is, the standard deviation increases as the sample concentration increases, as shown in Figure 1. Some curve fittings, such as four-parameter and five-parameter curve fitting, reduce the vertical error between data points and curves. As a result, during the curve fitting process, these points on the curve extend upward, and some data points may be missed at a lower concentration, so that the horizontal interpolation is inaccurate at low concentrations. Correct correction factors to weight the curve will overcome this problem and accurately predict the curve, so the most accurate concentration estimate comes from the weighted calculated value. Weighting factor At present, there are several weighting methods that can achieve the accuracy and accuracy of the curve fitting parameters reaching the predicted values. The primary weighting method adjusts the data 3 by adding an inverse factor: 1/Y 2 or 1/Y. 1/Y 2 relative weighting method, suitable for when the Y value is higher, the point at the upper end of the curve is more discrete, but the relative distance (distance / Y) is a constant, 1/Y is called Poisson weighting, which is suitable for the Y-value error of Poisson distribution, and the numerical dispersion is caused by the counting error. Other weighting methods to adjust the data can be added by the inverse factor with the concentration. 1/X 2 or 1/X. This will make the weight of the left part of the figure larger than the right side 4. The standard deviation weighting factor is inversed by 1/Std 2 , allowing more weight to be assigned to low-scattering data points. However, this approach is useful for reflecting differences in consistency when there are multiple parallel samples. The reciprocal of the sum of squares is used for changes in the Gaussian distribution or the Turkey BiWeight to reduce the effects of outliers. Other weighting methods are not detailed here. Use weighting factors in SoftMax Pro 7 software By default, SoftMax Pro® 7 software does not weight the curve fit. This is called a fixed weight, where the weighting factor is set to one of all data points of the curve fit. As shown in Figure 2, an overall fit and a single curve fit weighting operation can also be performed. Determine the best weighting factor in SoftMax Pro 7 software As discussed in the previous application note, “How to Choose the Best Curve Fitting Method in SoftMax Pro Softwareâ€, the best fit, and the best weighting method applied to the curve fit, you can use (SSE) And AKAIKE (AIC)'s method to measure the squared error used to detect curve fit. The template title "SoftMax Pro Weighting Factor Test" is applied to the most popular weighting factor method developed and implemented: 1/Y, 1/Y 2 and 1/Std 2 can be compared using the SSE and AIC methods. This template file can be downloaded directly from our website, such as As shown in Figure 3, an example of homoskedastic data that does not require any weighting is shown because the dispersion of its data is very small. The data uses a 5-P curve fit and applies various weighting factor approaches such as unweighted (Figure 3A), 1/Y (Figure 3B), 1/Y 2 (Figure 3C), and 1/Std 2 (Figure 3D) ). The next example shows the case of heteroscedastic data (Figure 6-8). Here, the standard deviation increases as the response increases, and scatter occurs (Fig. 7A). The data was subjected to a 5-P fit and various weighting factors were tried, without fitting (Figure 6A), 1/Y (Figure 6B), 1/Y 2 (Figure 6C) and 1/Std 2 (Figure 6D). The results are summarized in Figure 7, and show that the 1/Y2 factor approach is the best fit weighting method for the data set. in conclusion Test templates were developed using the SSE and AIC methods, and the curve fit model selected in the SoftMax Pro7 software tested the most common weighting factors. These statistical tests help to compare fit optimizations for different weighting factors and confidently choose the most appropriate weighting method. However, it must be ensured that there is enough data point support to explain its changes. 1. Gottschalk, P., Dunn, J. 2005. The5-Parameter logistic: A characterisation andcomparison with the 4-Parameter logistic, Analytical Biochemistry, 54-65.
Plant extracts refer to substances extracted or processed from plants (all or a part of plants) using appropriate solvents or methods, and can be used in the pharmaceutical industry, food industry, daily chemical industry and other industries.
There is a conceptual overlap between plant extracts and herbal extracts. The raw materials of plant extracts in my country are mainly derived from Chinese herbal medicines, so domestic plant extracts can also be called Chinese medicine extracts to some extent.
Herbal Extract,Liquid Herbal Extracts,Herbal Extract Powder,Natural Herbal Extract XI AN RHINE BIOLOGICAL TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD , https://www.rhinebiotech.com
- In a curve fitting chart, multiple curves can be customized in the same table user-defined standard and quasi-addition
- The weight factor detection template can be downloaded directly from the official website of softmaxpro.com 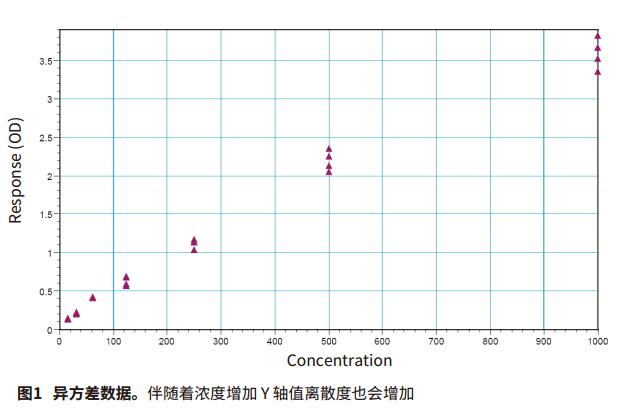
references
2. Ledvij, M. 2003. Curve fitting made easy, TheIndustrial Physicist.
3. Dolan, J., 2009. Calibration Curves, PartV: Curve Weighting, LC.GC.
4. Kiser, M., and Dolan, j. 2004. Selecting thebest curve fit, LC.GC Europe. 
