Using drip irrigation system fertilization can provide conditions for precise fertilization, very significant increase in fertigation, irrigation efficiency, reduce production costs, increase production, quality, and ultimately improve economic efficiency. Drip irrigation technology has been widely promoted around the world and is very popular. Through drip irrigation system fertilization, on the one hand, as the soluble fertilizer is applied directly to the crop root accumulation area with drip irrigation, there is no fertilizer waste on the crop field. Drip irrigation, on the other hand, is infiltrated into the root zone in the form of drip at a small flow rate and is very easy to control. Water and fertilizer will not have deep washing waste. Nitrogen application by drip irrigation can reach up to 74%, while the traditional method of casting will not exceed 30%. The disadvantage of fertigation with drip irrigation systems is that it is possible to plug the emitters. Fertilizer must be soluble, insoluble fertilizer will quickly plug the dripper. The chemical reaction between the raw materials of the fertilizer will also produce precipitation. Over time, the sediment will clog the drip irrigation system. The uniformity of fertilization depends on the uniformity of irrigation. If the uniformity of the drip irrigation system is high, the evenness of fertilization is also high. Therefore, the uniformity of drip irrigation is a very important indicator and every effort should be made to improve uniformity of drip irrigation: 1: Fine design, irrigation system 2 : Pressure-Compensated Dripper 3: Adding Regulators in Appropriate Position of Pipeline Fertilizer solubility Use drip irrigation system fertilization, we must carefully study the solubility of fertilizers. Insoluble, low solubility, or easily react under certain conditions, the precipitated fertilizer is avoided. Most solid fertilizer coating. In order to avoid clogging of the drip irrigation system by the coating, it is advisable to select a small amount of the sample and stir it in the dissolving tank before observing the dissolution of the coating. If the dissolved coating material precipitates to the bottom of the tank, at the time of application, let the composter draw the upper solution and do not agitate the entire fertilizer solution. Urea, nitric acid, calcium nitrate, and potassium nitrate absorb heat from the water when dissolved, and the temperature of the water is greatly reduced. At this point, the dissolved amount may not reach the required amount. In order to fully dissolve, it is best to allow the solution to stand for a few hours. As the temperature rises, the remaining undissolved portion gradually dissolves and can be injected into the system. Before the injection, observe the test first to assess the possibility of plugging the dripper. Some fertilizers should be dissolved in the fertilizer for 1-2 hours to see if there is a precipitate and how much sediment is deposited. If dissolved in water for several hours and the solution is still chaotic, it may block the drip irrigation system. If several kinds of fertilizers are applied at the same time, they should be sampled before injecting into the system. At the same time, they should be put into the observation tank at the same time to observe the dissolution after mixing, and then decide whether to inject at the same time. Second, nitrogen application drip irrigation system Nitrogen fertilizer is the most commonly used fertilizer applied by drip irrigation systems. Nitrogen fertilizers generally have good water solubility and are easily applied to the root zone of crops as irrigation water trickles into the soil. However, if you do not control it properly, it is easy to produce washing loss. Due to the small drip flow rate (single emitter: 4-8 l/h), it is very easy to control the leaching loss. If irrigation and fertilization are all automatically controlled, the rinsing damage can be completely avoided. Among all nitrogenous fertilizers, urea and ammonium nitrate are most suitable for drip fertilization. Because the risk of plugging with these two fertilizers is minimal, ammonia is generally not recommended for drip fertilization because ammonia increases the pH of the water. An increase in pH results in precipitation of calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus in the irrigation water and clogging of the dripper. Ammonium sulfate and calcium nitrate are water soluble, but they also have a risk of plugging. If nitrogen is continuously applied and the irrigation system stops pumping, the nitrogen in the water in the irrigation system will remain for a long time. At this time, the presence of nitrogen will nourish the growth of microorganisms in the system and eventually block the dripper. Third, drip irrigation phosphorus Phosphorus is not as active in soil as nitrogen. In general, the volatilization of phosphorus is lost, and the loss of leaching is less than nitrogen. Phosphorus is needed early in most crops. Therefore, phosphate fertilizer should be applied before planting or when planting. In the production phase, if there are signs of phosphorus deficiency, injecting phosphate fertilizer into irrigation water can also supplement the deficiency of phosphorus. Injecting phosphate fertilizer may clog the drip irrigation system. Due to the reaction of water and phosphate fertilizers, solid precipitates in the water, causing clogging. Most solid-state phosphate fertilizers cannot be injected into irrigation systems such as phosphorus ammonia because of their low solubility. Ammonium monophosphate, potassium diphosphate triphosphate, phosphoric acid, phosphates and other phosphate fertilizers are soluble. Phosphor ammonia is high in calcium, and injection into irrigation water can often cause precipitation, which may cause clogging. The formed precipitate is very difficult to dissolve, and when the phosphorus and calcium ions are in solution, it will form divalent or trivalent calcium phosphate. The solubility of this salt is very low. Similarly, phosphorus and magnesium will form magnesium phosphate that is insoluble in water and can easily clog drip irrigation systems. Phosphoric acid is sometimes injected into the drip irrigation system. In addition to applying phosphorus to crops, it can also reduce the pH of irrigation water. Lowering the pH can avoid sedimentation. Lowering the pH can avoid sedimentation. The method to reduce the PH value is to add appropriate sulfuric acid, phosphoric acid, and the PH value can be reduced to less than 4.0. However, if you inject phosphoric acid for a long time, it will lead to zinc deficiency. It is generally injected only when the combined concentration of calcium and magnesium in the water is less than 50 ppm and the concentration of bicarbonate is less than 150 ppm. Fourth, drip irrigation potassium Potash is soluble and has been successfully injected into drip irrigation systems. The problem that may arise is that when potassium fertilizer is mixed with other fertilizers in a fertilizer tank, sediment may be generated and the sediment may clog the drip irrigation system. The commonly used potassium fertilizers for drip fertilization are: potassium chloride (KCI) and potassium nitrate (KNO3). Potassium phosphate should not be injected into the drip system and its solubility should be low. Five, drip irrigation fertilization recommended fertilizer 1. Ammonium nitrate solution (20-0-0) NH4NO3-H20 Citrus drip irrigation often fertilizer 2. Urea + Nitramine Solution (32-0-0)(NH2)22CO-NH4NO3 Be careful not to inject a piece of calcium nitrate, or to produce sediment 3. Calcium Nitrate (15.5-0-0-19N-PK-Ca) 5Ca (NO3)2-NH4-10H2O 4. Phosphoric acid (0-54-0)H3P04 Do not inject phosphoric acid with any calcium-containing fertilizer to avoid forming insoluble calcium phosphate and clogging the drip irrigation system. 5. Potassium chloride (0-0-62) KCL Because it is cheap and soluble in water, it is a commonly used potash fertilizer for drip irrigation. 6. Potassium nitrate (13-0-46) KNO3 Potassium nitrate is high in price, but it has no waste. Applying both nitrogen and potassium will be very beneficial to citrus production. Solubility is not as good as potassium chloride. However, it is more soluble than potassium sulfate. 7. Potassium sulfate (0-0-52)K2SO4 One of the commonly used fertilizers for drip irrigation and fertilization. In areas with high soil salinity, potassium sulfate is often used instead of potassium chloride. Its solubility is not as high as potassium chloride and potassium nitrate. 8. Sulfuric acid H2PO4 Sulfuric acid is not a fertilizer. Non-NPK is mainly used to control the pH when the water is rich in bicarbonate (can be reduced to 6.5-7.0). 9. Solid urea (46-0-0) or urea solution (23-0-0) Note: Do not inject urea and sulfuric acid Sixth, other matters needing attention 1. Injecting chemical fertilizers will produce corrosion effects on filters, valves, etc. Each injection must be filled with sufficient time to flush the entire system. There should not be any fertilizer solution remaining in the system. Fertilizer tanks should be cleaned after each injection. 2. If a suction pump is used, the fertiliser tank is preferably equipped with a stirrer. Fertilizer should be mixed before each fertilizer and fertilizer to accelerate dissolution. 3. Do not add too much fertilizer at a time. With drip irrigation, it is best to use a small amount of multiple methods. Applying too high a concentration of fertilizer to the soil is detrimental to the growth of the crop. 4. All fertilizers to be injected must be soluble. Also pay attention to the reaction between different fertilizers. Precipitates from the reaction may clog drip irrigation systems. Nitrogen fertilizers rarely cause plugging. The possibility of blockage caused by phosphate fertilizers is very high. Be careful. Injecting phosphoric acid is usually the safest. Potassium fertilizers can be quickly dissolved and generally do not contain plugging problems.
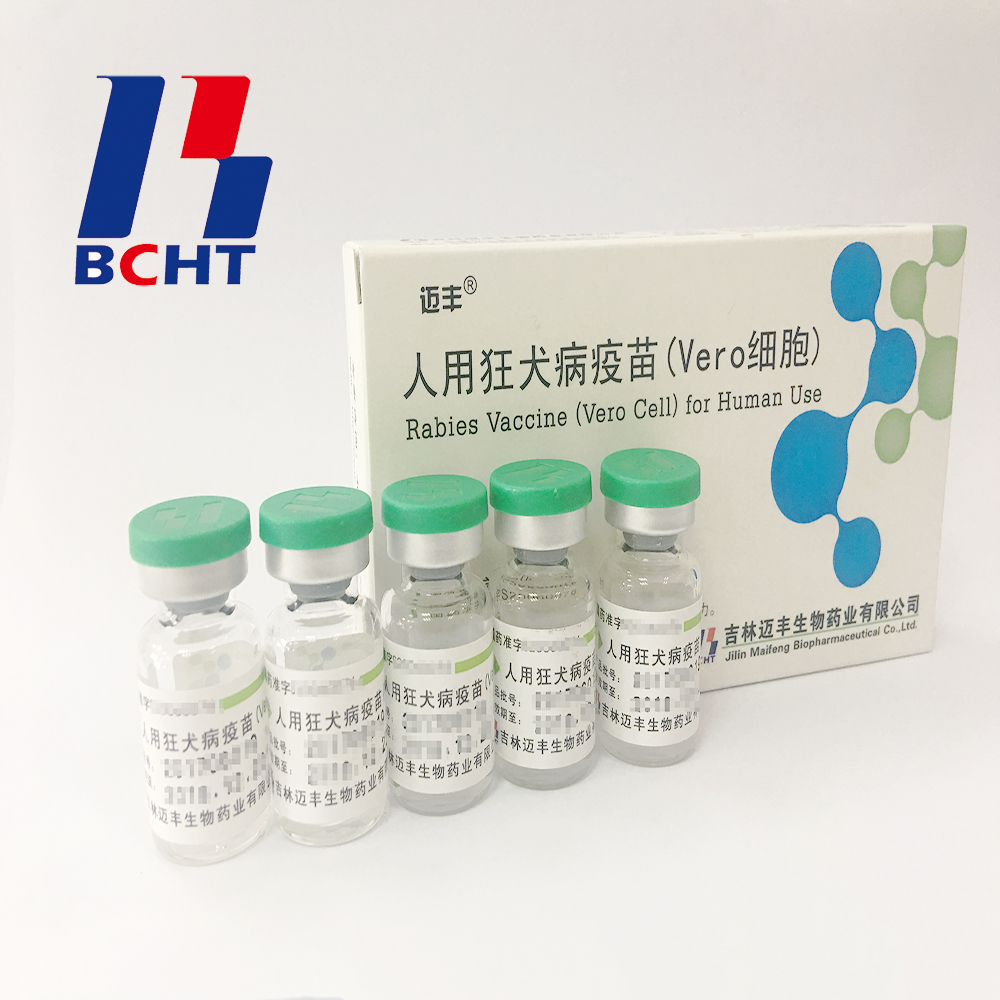
Jilin Maifeng Biopharmaceutical Co., Ltd., a subsidiary of BCHT, is devoted to mostly R&D in high density cell culture technique and its application for large scale production. Jilin Maifeng is the first company to develop and apply the self-developed microcarrier bioreactor technology to produce Rabies Vaccine For Human Use.
Rabies Vaccine For Human Use Biotechnology Bioproducts Preventive,Final Bulk Medicine Preventive,Final Bulk Pharmaceutical Preventive,Vaccine Biological Products Preventive Changchun BCHT Biotechnology Co.,Ltd , https://www.ccbcht.net