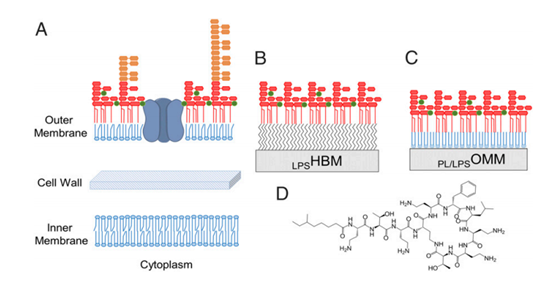
The bacterial outer membrane in the liquid crystal state is essential for antibiotic sensitivity November 02, 2018 Source: Ministry of Science and Technology In 1929, Alexander Fleming first published an article on antibiotics on the antibacterial effect of Penicillium cultures, so this year was called the "first year of antibiotics." In 1944, penicillin was first produced in the United States, and was immediately put into World War II to treat soldiers infected with injuries, saving countless lives. Therefore, people have combined penicillin with atomic bombs and radars as the three major inventions in the Second World War. Thus, people recognize the important role of antibiotics in clinical treatment. Subsequently, chlortetracycline (1947), chloramphenicol (1948), oxytetracycline (1950), nystatin (1950), erythromycin (1952), kanamycin (1958) A series of antibiotics were discovered and used in clinical medicine. On October 18, 2011, the Chinese Ministry of Health said that in China, the use rate of antibiotics for patients reached 70%, twice that of European and American countries, but it really needs less than 20%. The abuse of antibiotics leads to an increase in the body's resistance. Therefore, addressing the body's resistance has become the focus of research at this stage. Figure 1 Interaction of polymyxin B (PmB) with these in vitro semi-permeable membrane models Unlike the thick peptidoglycan cell wall of Gram-positive bacteria, Gram-negative bacteria possess a semi-permeable membrane composed of lipopolysaccharide and phospholipid molecules and have a selective barrier function. In order to kill Gram-negative bacteria, most antibacterial drugs (such as β-lactams) function mainly through the pores of proteins used to take up water-soluble nutrients into the cells (Fig. 1A). Mutations in the protein pores on semi-permeable membranes are an important cause of the body's resistance. Therefore, studying the relationship between the permeability of semi-permeable membranes and antibiotics is a prerequisite for the development of effective antimicrobial agents. Recently, scientists from the Cell and Molecular Biosciences Institute in the UK have simulated the same semi-permeable membrane composed of lipopolysaccharide and phospholipid molecules in vitro, and discussed polymyxin B (PmB) on this basis. Interaction with these in vitro semi-permeable membrane models (Figures 1B and C). The research results have recently been published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. The researchers in this paper sequentially transferred the phospholipid monolayer and lipopolysaccharide monolayer from the air-water interface to the solid substrate to produce an in vitro asymmetric phospholipid-lipopolysaccharide semipermeable membrane model, which was modified by other methods to make the membrane structure model. It is consistent with the value of the asymmetric phospholipid-lipopolysaccharide bilayer on the solid substrate of the previous study, thus ensuring the scientific nature of the experiment. In vivo studies have shown that the use of PmB results in damage to the semi-permeable membrane, manifested by the loss of the blister and lipopolysaccharide resulting in the rupture of the semi-permeable membrane. Therefore, it is proposed that PmB can form a channel with lipopolysaccharide to promote the passage of macromolecular substances through the semi-permeable membrane. The underlying mechanism is attributed to the replacement of the divalent cations necessary to bridge the negative charge of adjacent lipopolysaccharide molecules by PmB. The researchers monitored the data changes of the semi-permeable membrane after PmB use by Fourier transform attenuated total reflection infrared spectroscopy and confirmed the viewpoint that Pmb replaces divalent cations. PmB is embedded in the biofilm by substitution, which increases the permeability of the biofilm and promotes the uptake of foreign substances by the cells. Lipopolysaccharides in biofilms play an important role in regulating semi-permeable membrane molecular sieves against the penetration of antibiotics into the interior of cells. In the future, the interrelationship between lipopolysaccharide and outer membrane proteins will need to be further studied, especially the dynamic changes in protein production in semi-permeable membranes. In summary, this result demonstrates that the semi-permeable membrane of Gram-negative bacteria exhibits a tightly packed liquid crystal phase at its adapted growth temperature. Comparison of different in vitro models suggests that lipopolysaccharide plays a very important role in the study of the interaction of semipermeable membranes with antibiotics. living room lounge chairs,Living Room Chairs,living room half recliner chairs Guangdong Widinlsa International Co.Ltd , https://www.gdwidinlsa.com