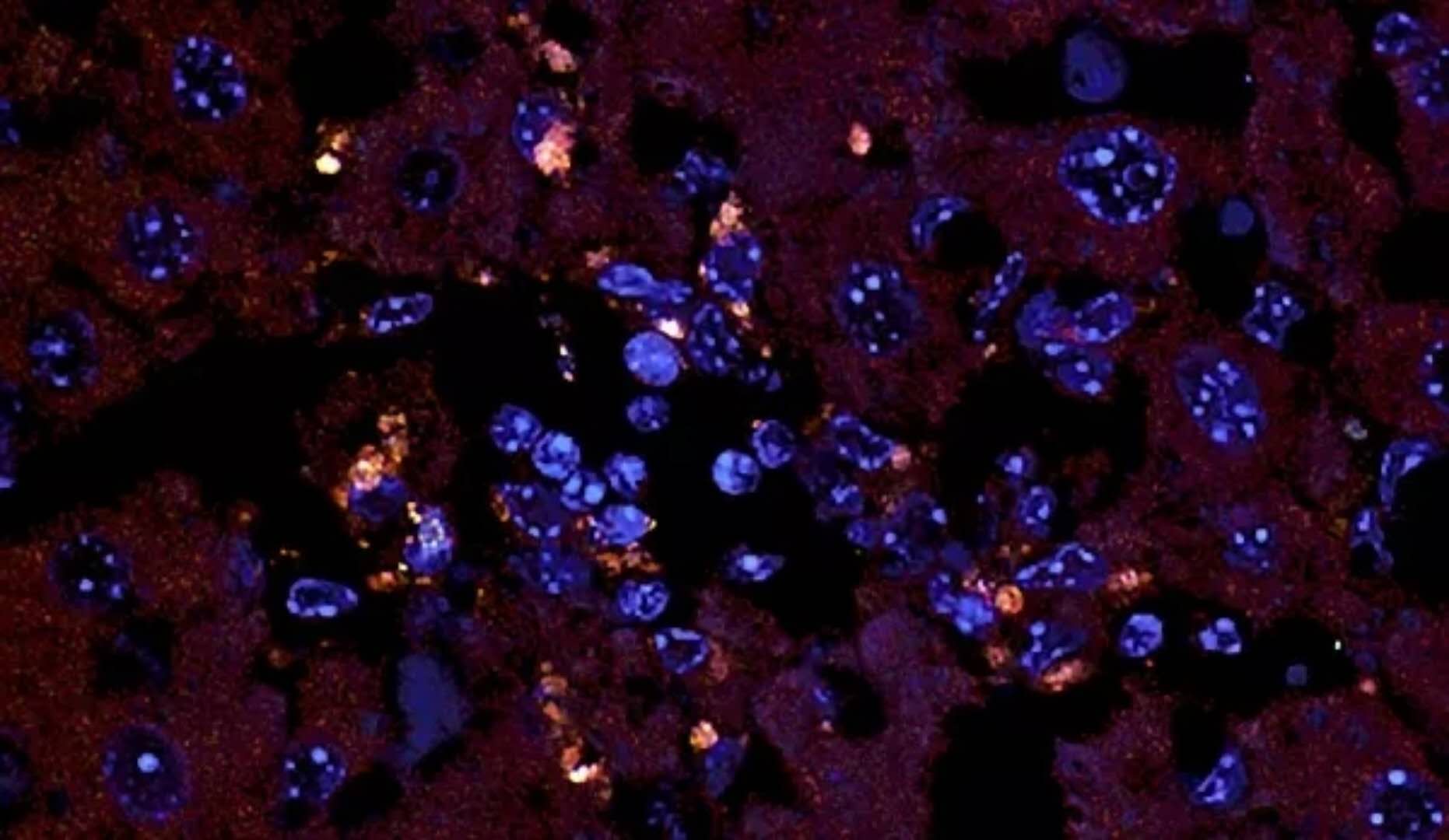
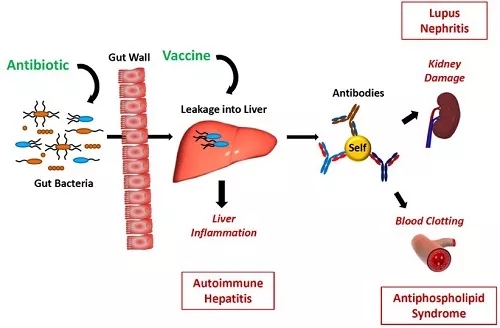
Science: Intestinal bacteria also "do evil" - triggering autoimmune diseases March 12, 2018 Source: Biological Exploration We often say that we have to "divide into two" to look at the problem. This is not the case. Xiaobian has just been in "Science's heavy results: high dietary fiber can improve diabetes, and intestinal bacteria "have made meritorious deeds"! The article introduces the benefits of intestinal bacteria, and scientists have seized evidence of intestinal bacteria "doing evil" in another Science paper published on the same day! Image source: Science (DOI: 10.1126/science.aar7201) In recent years, more and more studies have shown that intestinal bacteria living in the human body are associated with a range of diseases, including autoimmune diseases in which the immune system attacks healthy tissues. To clarify this connection, a research team at Yale University focused on a bacterium called Enterococcus gallinarum. It was found that the bacteria spontaneously migrated outside the intestine into the lymph nodes, liver and spleen. Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) image of the gut commensal E. gallinarum translocated into the liver tissue of autoimmune mice. Orange dots represent the bacterium. Credit: Manfredo Vieira et al., Science (2018) Using the mouse model, the scientists observed that in these tissues outside the gut, E. gallinarum initiates the production of autoantibodies and inflammation, both of which are characteristic of autoimmune responses. In hepatocytes cultured in healthy individuals, they confirmed the same inflammatory mechanism. At the same time, the study found that the bacteria are also present in the liver of patients with autoimmune diseases. An oral antibiotic or a vaccine into the muscle that is directed against E. gallinarum prevent autoimmune diseases to occur. Credit: Martin Kriegel Through further experiments, the team confirmed that antibiotics or vaccines against E. gallinarum can be used to inhibit autoimmunity in mice. Both methods are capable of inhibiting the growth of bacteria in tissues and impairing their effects on the immune system. Dr. Martin Kriegel, author of the paper, said: "The vaccine against E. gallinarum is a special method. It is administered intramuscularly, in order to avoid targeting other bacteria in the intestine. When blocking causes inflammation In the pathway, we successfully reversed the impact of E. gallinarum on autoimmunity." Kriegel and colleagues plan to investigate E. gallinarum and its related mechanisms further. They believe that treatment with antibiotics and other methods (such as vaccines) is a promising way to improve the lives of patients with autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus and autoimmune liver disease. References: 1) The enemy within: Gut bacteria drive autoimmune disease
The plastic beaded seals have a beaded tail. When the tail goes through the locking hole, the locking mechanism provides a strength to stop its entrance.
The plastic beaded seals are adjustable indicative plastic security seal ideal for sealing varying sized items.
The applications for beaded seals include: Trailer Doors, Bulk Tankers, Railcars, Tote Boxes, Fibre Drums, Storage Cabinets. The material is high Density Polyethylene and Acetal. The marking can be Hot Stamped Printing or laser engraving.
Plastic Beaded Seals,Plastic Beaded Seal,pull tight seals,Plastic Locking Mechanism Seals Wenzhou Haoshi Light Industrial Products Co., LTD , https://www.economicseals.com