This project Gannan quality navel orange whole fruit (not peeled) as raw materials, using self-developed patent Orange surface sterilization technology to maximize retained a whole pieces of all Orange essence (Orange: Shun Qi, phlegm, pulp: fiber laxative, fruit seeds: allergic inflammation, juice: whitening detox).
I produced using enzymes navel cleaning, sterilization, slice, fermentation (fermentation grade composite multi-strain), solid-liquid separation, bottling and other steps. Each step developed a patented automated production equipment, fully automated production, to avoid the traditional manual production workers are not standardized, easy to pollution, low production efficiency, product quality is unstable defects.
Companies registered capital of 35 million yuan, the end of 2014 the total assets of 48.69 million yuan, including fixed assets of 37.52 million yuan. The company's existing cooperation Orange cultivation base 7043.5 acres, the company production base is located in Jiangxi County Tech Industrial Park Chu Tan industrial area, covers an area of 120 acres, it has built a standard plant 9,000 square meters, Nissan 6000 kg Orange enzymes and other liquid enzyme products. Enzyme, known as enzyme, refers to a polymer substance having biocatalytic functionality. In the catalytic reaction system an enzyme, the reactant molecules are known as substrates, enzyme substrates by catalytic conversion to another molecule. Almost all cellular activity of enzymes involved in the process are required to improve efficiency. Similar to other non-biological catalysts, enzymes chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy to accelerate the rate of the reaction, most of the enzyme catalyzed reaction rate can be increased a million times; in fact, the enzyme is to provide an activation energy needs than another low way, so that more particles to have less than the activation energy of the reaction kinetic energy, thus speeding up the reaction rate. Enzyme as a catalyst, in itself is not consumed during the reaction, it does not affect the chemical equilibrium reactions. Positive enzyme catalysis, but also a negative catalytic effect, not only to accelerate the reaction rate, but also to reduce the reaction rate. And other non-living catalysts is different, having a high degree of specificity of enzyme, only a catalytic reaction or produce a particular specific configuration.
Orange Enzyme Solution,Enzyme Essence Liquid,Fresh Orange Fermentation Ganzhou Green days Biochemical Technology Shower folder mechanic Co., Ltd. , https://www.cn-gangdao.com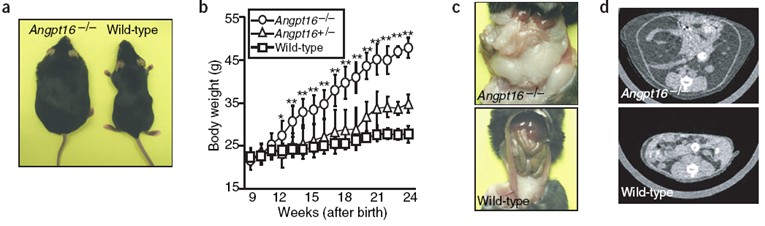
Conventional enzyme production is mainly produced by hand, hand-sliced, hand-fermentation, the company every step of the process are used self-developed technology and equipment to automate production. Moreover, the conventional enzyme production have adopted a fermentation technology, enzyme often taste discomfort, sour and other issues, I produced using a variety of enzymes, probiotics composite grade fermentation technology, fermentation at different times with different strains, and two or three times through fermentation, enzymes such pure taste, streptozotocin balanced nutrients. Scientific and standardized process:
Application of small animal CT (LCT200) in mouse obesity research
Study on the role of angiopoietin-related growth factor AGF in mouse obesity using small animal CT (LCT200)
one. Summary
The angiogenin-related growth factor AGF is a member of the angiopoietin-like protein family, which is secreted mainly from the liver to the systemic circulatory system. This study showed that more than 80% of AGF-deficient mice died on the 13th day of embryonic stage, and compared with the control group, the surviving mice showed significant obesity and had skeletal muscle and liver. Lipid accumulation, while reducing energy consumption, and resistance to insulin. In addition, AGF-activated mice are leaner, consume more energy, and are more sensitive to insulin. A high-fat diet does not cause obesity or insulin resistance in these mice, nor does it cause steatosis in non-adipose tissue. Overexpression of AGF in the liver (approximately 2.5-fold increase in AGF serum concentration) and a high-fat diet in mice resulted in significant weight loss and increased insulin resistance in mice. The above results indicate that, as a new hepatic circulation factor, AGF has an effect of inhibiting obesity and reducing obesity-related insulin resistance.
two. Partial experimental results
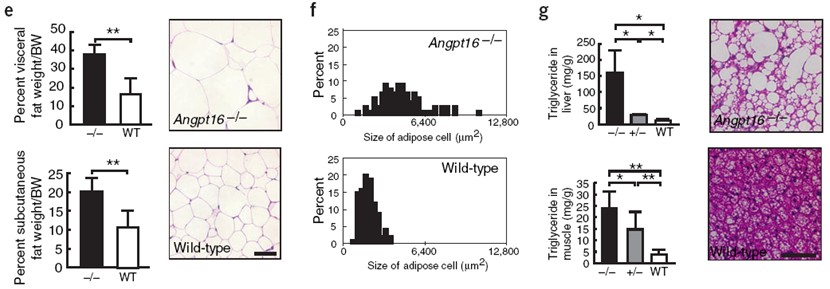
After 12 weeks of birth, Angptl6 −/− mice showed significant weight gain compared to wild-type mice under normal dietary conditions (Fig. 1b), while there was no significant weight difference between female and male mice. The small animal CT (Aloka Latheta LCT200) tomography showed that after 8 months of birth, the amount of abdominal fat and subcutaneous fat in Angptl6−/− mice was significantly higher than that in wild-type mice (Fig. 1c–e). The size of adipocytes in the two groups was also significantly different (Fig. 1e, f). Compared with the control group, the liver, skeletal muscle and brown adipose tissue of Angptl6−/− mice accumulated more lipids (Fig. 1g).
Figure 1 . Angptl6 −/− The obesity of mice under normal diet.
(a) Comparison of knockout mice with normal mice; (b) Comparison of body weights of different genotypes (n = 8); (c) (d) Abdominal physiological anatomy of different genotype mice and micro-CT ( LCT200) tomographic images; (e) percentage of body weight of subcutaneous fat and visceral fat and (as measured by LCT200 analysis software) (f) cell distribution; (g) triglyceride levels.
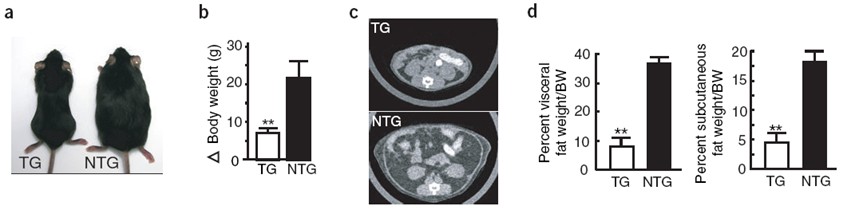
To investigate whether Angptl6 transgenic mice are resistant to obesity, we fed a 8-week-old mouse with a high-fat diet containing 32% fat for 12 weeks to fatten the mice. The Angptl6 transgenic mice fed in this manner showed significant differences from the control group: at the end of feeding, the net weight gain of the transgenic and control mice was 7.13 ± 1.03 g and 21.86 ± 4.03 g, respectively (Fig. 5a, b) ). As we expected, the high-fat diet caused a large accumulation of fat in abdominal fat and subcutaneous fat tissue in the control mice, but not in transgenic mice (Fig. 5c, d). It is worth noting that the WAT of the transgenic mice was significantly smaller than the WAT in the control group (Fig. 5e). In transgenic mice, there was no significant accumulation of fatty acids in BAT, liver and skeletal muscle, whereas steatosis occurred in control mice (Fig. 5e, f). There was no significant difference in blood glucose levels between the two groups (Fig. 5g).
Figure 5 Resistance of high fat obesity and metabolic abnormalities in transgenic mice
( a ) AGF transgenic mice (TG) and non-transgenic control mice (NTG) after a 3-month high-fat diet; ( b ) changes in body weight of TG and NTG mice after a 3-month high-fat diet ( n = 10); ( c ) Comparison of CT scan images of the two groups of mice; ( d ) Analysis of the percentage of visceral fat ( n = 10) and subcutaneous fat ( n = 10 ) in different genotype mice using LCT200 analysis software
three. in conclusion
This study demonstrates for the first time that AGF can directly inhibit obesity and resist insulin resistance associated with obesity. In addition, we speculate that AGF-induced angiogenesis can accelerate energy metabolism. Therefore, AGF is an important potential target for the development of anti-obesity drugs and drugs for the treatment of metabolic disorders.
Selected from: Angiopoietin-related growth factor antagonizes obesity and insulin resistance
VOLUME 11 | NUMBER 4 | APRIL 2005 NATURE MEDICINE.